What is a Pivot Point?
What is a Pivot Point?
Standard Pivot Points are the default setting and the parameters box is empty. Chartists can apply Fibonacci Pivot Points by putting an “F” in the parameters box and Demark Pivot Points by putting a “D” in the box. Knowing the location of the pivot range at all times allows you to keep your finger on the pulse of the market and provides you with a significant trading edge. The pivot point focuses on the closing price relative to the bar with the highest High (or lowest Low).
Stochastics: An Accurate Buy and Sell Indicator
Day traders will use pivot points as a way to determine when market sentiment has gone from bullish to bearish or vice versa. The Ease of Movement technical indicator shows the relationship between price and volume, and is often used to assess the strength of an underlying trend.
It is put forth in the current period as the first important level. A move above the Pivot Point suggests strength with a target to the first resistance. A break above first resistance shows even more strength with a target to the second resistance level. Demark Pivot Points start with a different base and use different formulas for support and resistance.
After the horizontal support was broken, the same line provided resistance for the price at points and , signalling potential short setups. When the price reaches a key resistance level, sellers may jump into the market and send the price lower again. Key chart levels are important technical levels at which a financial instrument could face increased buying or selling pressure.
Traders look out for key chart levels to place their buy and sell orders around those lines, which accelerates price-moves and increases volatility when the price reaches those levels. Typically, key chart levels are identified by support and resistance lines, which act as barriers for the price when reached from the upside or downside, respectively. In this article, we’ll cover what key chart levels are, how to spot and trade them, and answer a few common questions that beginner traders have when it comes to support and resistance trading. Some authors have called the pivot range the “meat of the market”, while others refer to the central pivot point as the “heartbeat of the indicator”. In my opinion, the central pivot range is the Swiss Army Knife of pivots.
These Pivot Points are conditional on the relationship between the close and the open. Pivot Points for 30-, 60- and 120-minute charts use the prior week's high, low, and close. Once the week starts, the Pivot Points for 30-, 60- and 120-minute charts remain fixed for the entire week. The Pivots do not change until the week ends and new ones can be calculated.
These are basically mini levels between the main pivot point and support and resistance levels. Also, most of the time, trading normally takes place between the first support and resistance levels. Pivot points are based on a simple calculation, and while they work for some traders, others may not find them useful. There is no assurance the price will stop at, reverse at, or even reach the levels created on the chart.
Demark Pivot Points
Without row interchange in this case, rounding errors will be propagated as in the previous example. Pivot Points can be used to help determine where to draw trendlines in order to visualize price patterns. The longer the trend (the higher the period selected) before and after the Pivot Point, the more significant the Pivot Point.
- That is, this indicator is usually color-coded to indicate whether you should buy or sell at certain pivot points.
- The pivot point focuses on the closing price relative to the bar with the highest High (or lowest Low).
- These are basically mini levels between the main pivot point and support and resistance levels.
- Pullbacks work because support and resistance levels change their roles once broken.
- If you’re serious about your career as a trader, you need to learn how to trade support and resistance levels early in your trading career.
Like any technical tool, profits won't likely come from relying on one indicator exclusively. If the pivot point price is broken in an upward movement, then the market is bullish. If the price drops through the pivot point, then it's is bearish.
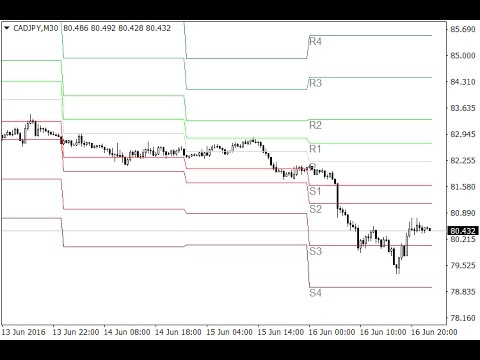
The chart below shows the Russell 2000 ETF (IWM) with Demark Pivot Points on a 15-minute chart. Notice that there is only one resistance (R1) and one support (S1). Demark Pivot Points do not have multiple support or resistance levels.
Zig Zag indicator is used to identify price trends and changes in price trends. The indicator lowers the impact of random price fluctuations, highlighting underlying bull and bear power.
For stocks, which trade only during specific hours of the day, use the high, low, and close from the day's standard trading hours. Next, multiply the previous day’s range with its corresponding Fibonacci level.
Simply put, the Camarilla Equation is a price-based indicator that provides a series of support and resistance levels, much like the Floor Pivots indicator. However, what makes this indicator unique is the fact that each pivot carries a specific call to action.
Moving averages are a technical indicator which takes the average price of the last n trading periods and plots it on the chart. While simple moving averages give an equal weight to all trading periods included in their calculation, exponential moving averages give more importance to the most recent price-data. If you’re serious about your career as a trader, you need to learn how to trade support and resistance levels early in your trading career. There are many types of key chart levels which act as important support and resistance levels in the chart.
The Pivot Point is in the middle, the support levels (S1, S2, and S3) are below and the resistance levels (R1, R2 and R3) are above. The Woodie pivot point, support levels, and resistance levels are the solid lines while the dotted lines represent the levels calculated through the standard method.
Other times the price will move back and forth through a level. As with all indicators, it should only be used as part of a complete trading plan. Not all support and resistance levels work the same or produce trade setups with equal probability of success. Here’re some pro tips on increasing the likelihood that a trade based on key support and resistance levels becomes a winner. Points and acted as resistance and support for the EUR/USD pair, respectively, identified by a simple rising channel.
It is a leading indicator providing advanced signaling of potentially new market highs or lows within a given time frame. To increase the likelihood of profitable trades, first mark key support and resistance levels on higher timeframes, such as the 4-hour and daily ones.
They are used in finding uptrends and downtrends in the market by connecting higher lows in uptrends and lower highs in downtrends. If you’re just starting out with trading and technical analysis, you need to cover the market’s foundations.
Just like with rising channels, the lower boundaries of a downward sloping channel act again as support levels, while the upper boundaries act as resistance levels for the price. Channels are quite similar to trendlines, only that they include a second trendline which is drawn parallel to the first trendline. Support levels are price-lines at which the market had difficulties to break below, signalling that buyers may join the market again if the price falls to a key support level. Resistance levels are quite similar to support levels, only that they form to the upside and signal price-levels at which the market had difficulties to break above. On a final note, sometimes the second or third support/resistance levels are not seen on the chart.
Комментарии
Отправить комментарий